Understanding Cardiac Rehabilitation
12 September 2023
Cardiac rehabilitation (cardiac rehab) is a comprehensive program designed to help individuals with heart disease recover and improve their overall cardiovascular health.
Here are the key components and objectives of cardiac rehabilitation:
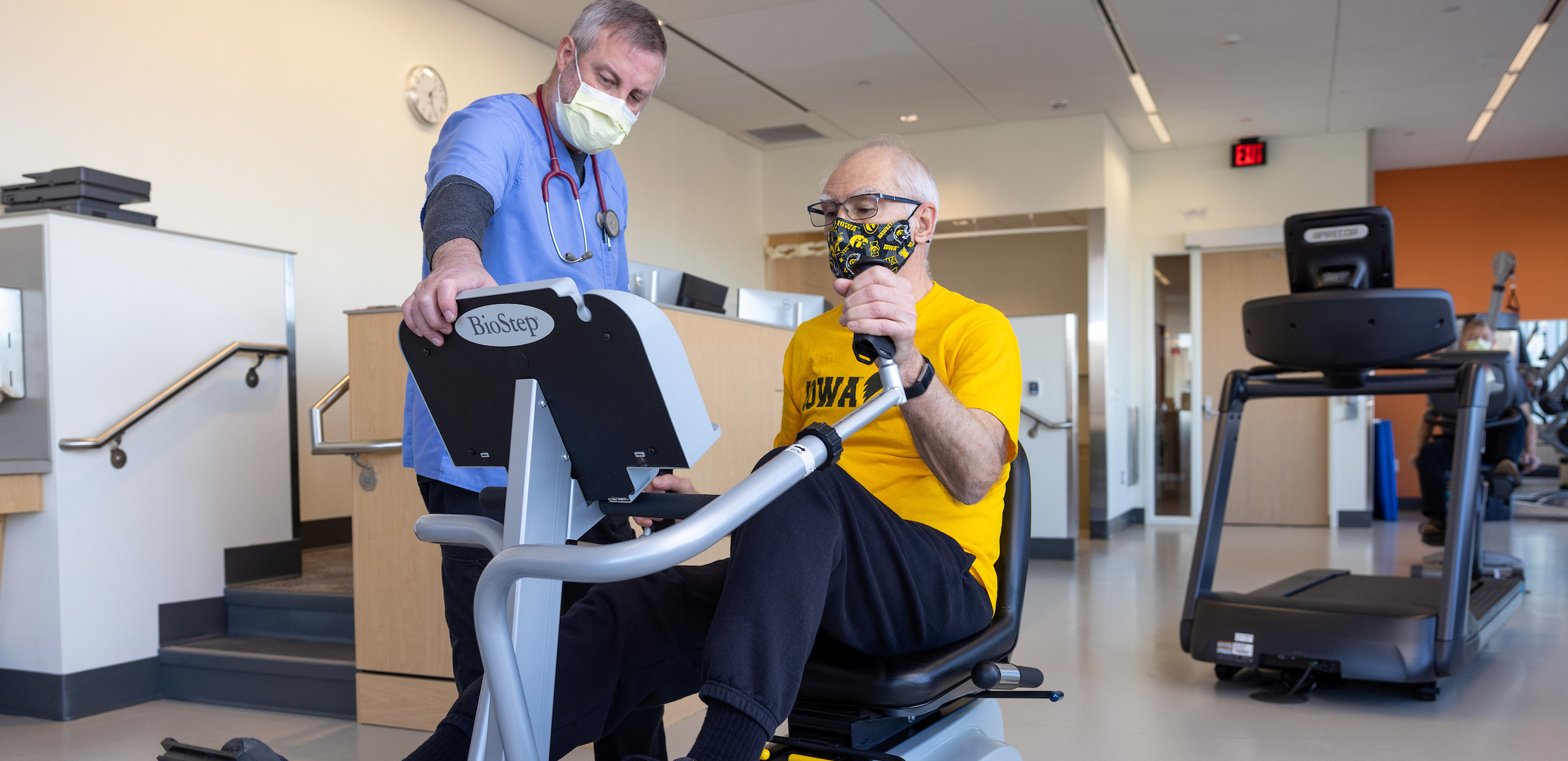
Medical Evaluation and Monitoring: The program starts with a thorough medical evaluation to assess the individual's heart health, including their current medical condition, risk factors, and fitness level. Throughout the program, participants are closely monitored by healthcare professionals, including nurses, doctors, and exercise physiologists.
Exercise Training: A structured exercise program tailored to the individual's specific needs and abilities is a central component of cardiac rehab. Exercise helps improve cardiovascular fitness, strengthen the heart, and reduce the risk of future heart problems. Participants usually engage in monitored aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises. Exercise sessions are gradually progressed to meet individual goals.
Education and Counseling: Cardiac rehab provides education and counseling on various aspects of heart health, including nutrition, medication management, stress reduction, and lifestyle modifications. Participants learn how to make healthier choices and manage risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Education also helps individuals understand their medications and the importance of adherence.
Psychosocial Support: Emotional support is essential for those recovering from heart-related events. Cardiac rehab programs often include counseling and support groups to address anxiety, depression, and stress that can be associated with heart disease.
Lifestyle Modification: Participants are encouraged to adopt heart-healthy behaviors, such as quitting smoking, managing their weight, and reducing salt and saturated fat intake. These lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of further heart problems.
Risk Factor Management: Cardiac rehab focuses on managing and controlling risk factors for heart disease, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity. Participants work with healthcare professionals to set and achieve specific goals for these risk factors.
Medication Management: Many individuals with heart disease require medications to control their condition. Cardiac rehab educates participants about their medications, helps ensure proper adherence, and monitors any side effects.
Long-Term Maintenance: The benefits of cardiac rehabilitation extend beyond the program's duration. Participants are encouraged to continue their healthy habits and exercise routines at home to maintain their heart health.
Individualized Care: Cardiac rehab programs are tailored to each participant's unique needs, taking into account their medical history, fitness level, and specific goals.
Cardiac rehabilitation is typically divided into phases, with Phase I starting in the hospital immediately after a heart event or surgery and progressing through Phase II (outpatient rehab) and Phase III (maintenance) in an outpatient or community-based setting. Participation in a cardiac rehab program c significantly improve quality of life, reduce the risk of future heart problems, and enhance overall well-being for individuals with heart disease. It's important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if cardiac rehab is appropriate and to find a program that suits individual needs.