Patient Safety
04 July 2023
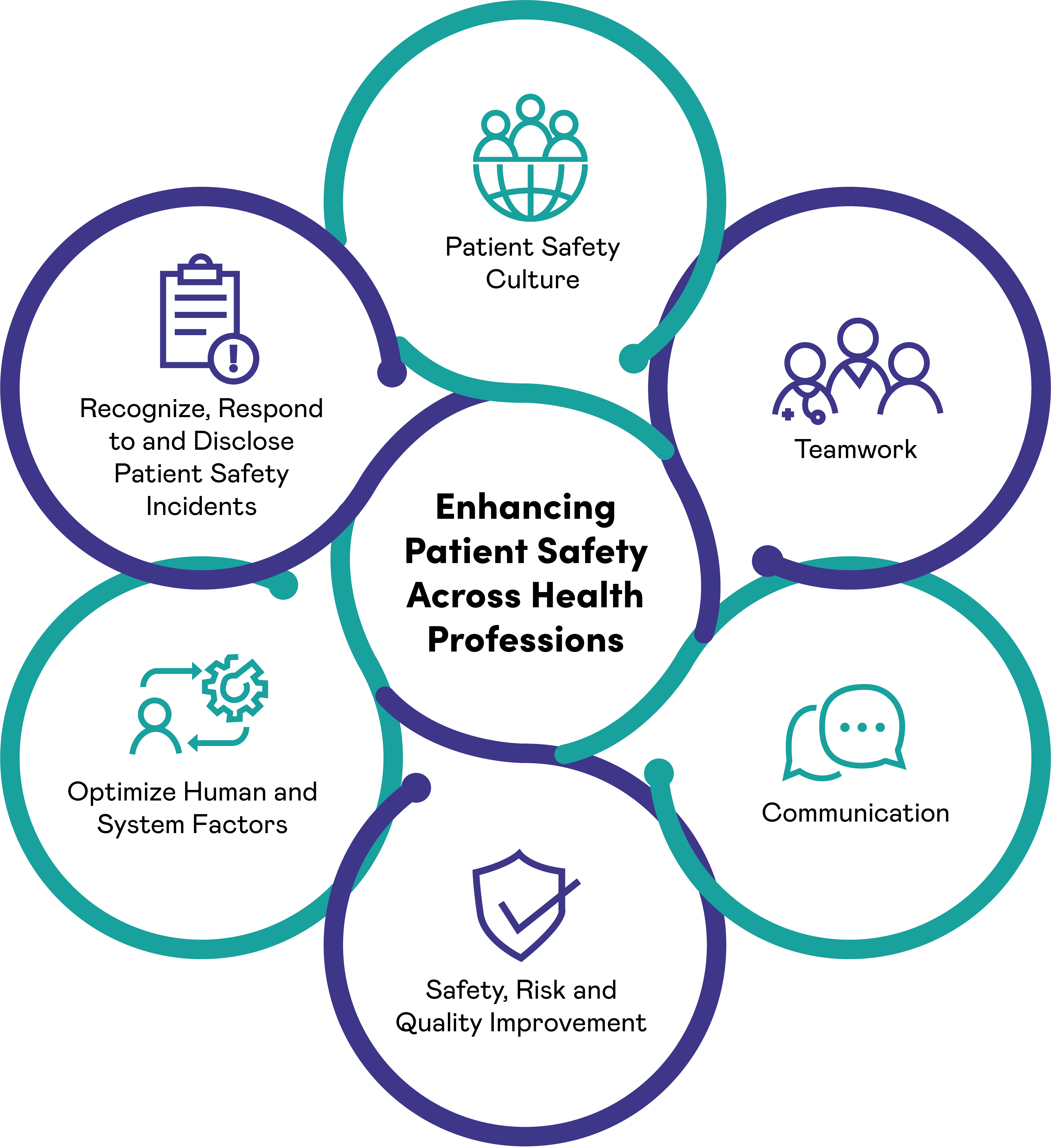
Patient safety is a critical aspect of healthcare that focuses on preventing harm to patients during their interactions with the healthcare system. It involves identifying and reducing risks, implementing safety measures, and creating a culture of continuous improvement to enhance the overall safety of healthcare delivery. Here are some key aspects related to patient safety:
Medical Errors: Medical errors are unintended acts or omissions that may lead to patient harm. They can occur at various stages, such as diagnosis, medication administration, surgical procedures, or communication breakdowns. Patient safety initiatives aim to minimize the occurrence of medical errors through improved systems, processes, and protocols.
Medication Safety: Medication errors, such as prescribing the wrong drug or dosage, administering medications incorrectly, or adverse drug reactions, can pose significant risks to patient safety. To enhance medication safety, healthcare providers utilize strategies like computerized physician order entry systems, barcode scanning, medication reconciliation, and patient education on medication use.
Infection Control: Preventing healthcare-associated infections is a critical aspect of patient safety. Healthcare facilities implement rigorous infection control measures, including hand hygiene protocols, proper sterilization and disinfection practices, and isolation precautions to minimize the risk of spreading infections among patients and healthcare workers.
Fall Prevention: Falls can cause injuries and complications, particularly among elderly or vulnerable patients. Patient safety efforts often include fall risk assessments, implementation of preventive measures like bed alarms, adequate lighting, and assisting devices, as well as patient and family education on fall prevention strategies.
Communication and Teamwork: Effective communication and teamwork among healthcare professionals are vital for patient safety. Clear and concise exchange of information, standardized communication tools (such as SBAR - Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation), and fostering a culture of open communication and collaboration contribute to reducing errors and improving patient outcomes.
Reporting and Learning from Adverse Events: Encouraging a culture of reporting and learning from adverse events is crucial in patient safety. Healthcare organizations implement systems for reporting incidents and near-misses, analyzing root causes, and implementing strategies to prevent similar events in the future.
Patient Engagement: Engaging patients in their care can contribute to improved safety. Patients are encouraged to actively participate in their healthcare decisions, ask questions, and provide important information about their health history, allergies, and preferences. Patient engagement also includes educating patients about their rights and encouraging them to speak up if they have concerns or notice any safety issues.
These are some of the key areas related to patient safety. Healthcare providers and organizations continuously work to implement strategies and best practices to ensure the highest level of safety for patients receiving care.